Introduction
Warts are benign growths on the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). While they are usually harmless, they can be unsightly and cause discomfort, particularly if located on pressure points like the feet or hands. This article delves into the types of warts, their causes, various treatment options, and preventive measures, providing an extensive understanding of wart removal.
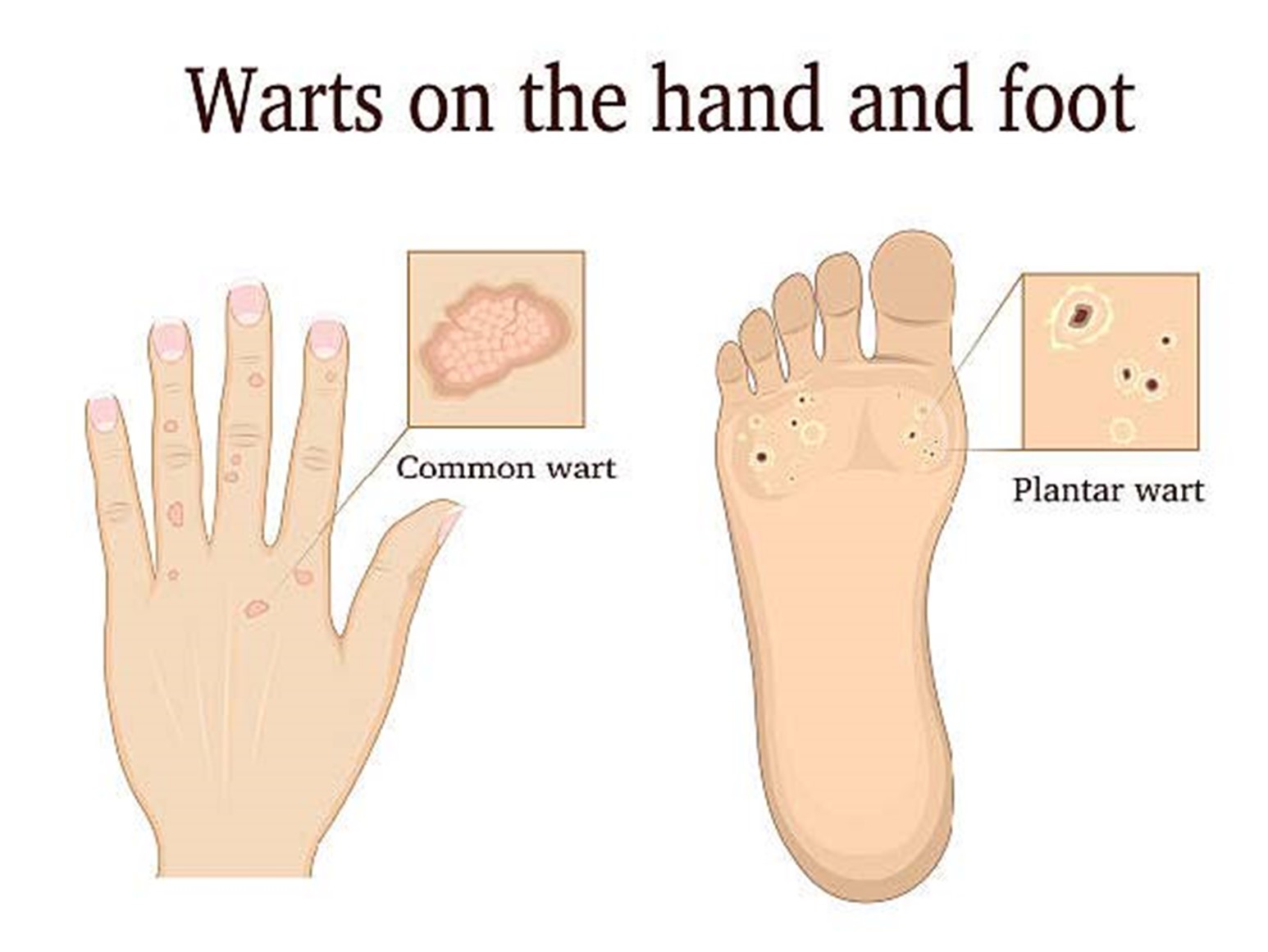
Understanding Warts
Warts can appear anywhere on the body, and their appearance varies based on their location and type. They are commonly classified into several types:
1. Common Warts (Verrucae Vulgaris)
Common warts are typically rough and raised, often found on fingers, knees, or elbows. They may be skin-colored or grayish and have a characteristic cauliflower-like appearance.
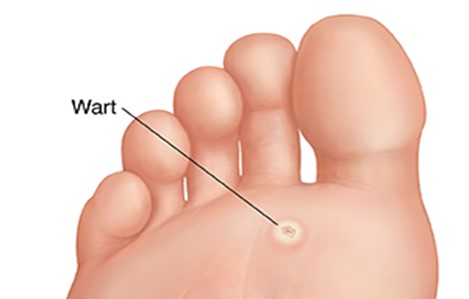
2. Plantar Warts
These warts develop on the soles of the feet and can be particularly painful due to their location. They are often flat due to pressure from walking and can have a hard center.
3. Flat Warts
Flat warts are smaller and smoother than common warts, usually appearing in large numbers on the face, neck, and arms. They can be slightly raised or flat and are often tan or light brown.
4. Filiform Warts
Filiform warts are thread-like and typically appear on the face, particularly around the mouth and eyes. They are elongated and can be flesh-colored or slightly darker.
5. Genital Warts
These warts appear in the genital and anal regions and are caused by certain strains of HPV. Genital warts require specialized treatment due to their location and potential to cause health complications.
Causes of Warts
Warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which infects the top layer of skin. The virus can enter through tiny cuts or breaks in the skin, leading to the formation of warts. HPV is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with a wart or by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus, such as gym floors or communal showers.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing warts:
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to HPV infections and the development of warts.
- Skin Injuries: Cuts, scrapes, or other skin injuries can provide an entry point for HPV.
- Age: Children and teenagers are more likely to develop warts, but they can occur at any age.
- Personal Habits: Nail-biting or picking at the skin can increase the risk of warts, especially around the nails.
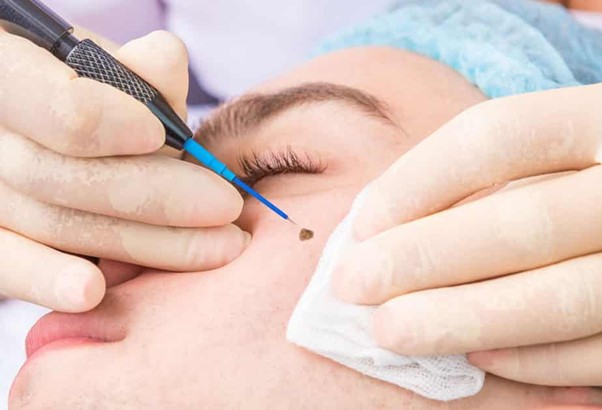
Treatment Options for Warts
While many warts resolve on their own without treatment, there are several options available for those who wish to remove them for cosmetic or comfort reasons. Treatment methods can vary depending on the type and location of the wart.
1. Over-the-Counter Treatments
Many over-the-counter (OTC) products contain salicylic acid, which helps dissolve the wart gradually. These treatments usually come in the form of gels, pads, or liquids. It’s essential to follow the instructions carefully and be patient, as it may take several weeks to see results.
2. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, causing it to fall off over time. This method is often performed in a doctor's office and may require multiple sessions for complete removal. Cryotherapy is effective for most types of warts but can be painful and may cause blistering.
3. Electrosurgery
Electrosurgery uses high-frequency electrical currents to destroy wart tissue. This method is particularly effective for larger warts or those that are difficult to treat with other methods. Electrosurgery is usually performed in a clinical setting and may require local anesthesia.
4. Laser Treatment
Laser treatment is an option for stubborn warts that do not respond to other treatments. This technique uses focused light beams to vaporize wart tissue. While effective, laser treatment can be expensive and may not be covered by insurance.
5. Surgical Removal
For larger warts or those that have not responded to other treatments, surgical excision may be necessary. This method involves cutting out the wart and surrounding tissue. It is typically done under local anesthesia and can leave a scar.
6. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy involves using medications that stimulate the immune system to fight the HPV infection. This treatment is usually reserved for persistent warts that do not respond to other therapies.
7. Home Remedies
Some people opt for home remedies for wart removal, such as:
- Duct Tape: Covering the wart with duct tape for an extended period may help remove it, although results can be inconsistent.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Applying apple cider vinegar to the wart may help due to its acidic nature, but it can also irritate the skin.
- Garlic: Applying crushed garlic may have antiviral properties that help in wart removal.
However, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider before trying home remedies, as they may not be effective and could cause skin irritation.
Preventing Warts
Preventing warts involves taking measures to avoid HPV infection. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Maintain Good Hygiene
- Wash Hands Regularly: Keeping hands clean can reduce the risk of spreading the virus.
- Avoid Touching Warts: Do not touch your own or someone else's warts, as this can lead to transmission.
- Wear Shoes in Public Places: Protect your feet in public pools, locker rooms, and showers to avoid plantar warts.
- Keep Feet Dry: Moisture can encourage the growth of warts, so it's crucial to keep your feet dry.
2. Avoid Sharing Personal Items
- Do Not Share Towels or Razors: Sharing personal items can spread the virus, so use your items only.
3. Boost Your Immune System
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can help strengthen your immune system.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is vital for overall health.
- Get Enough Sleep: Proper rest is essential for a strong immune system.
When to See a Doctor
It’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider if:
- The wart changes in appearance or color.
- You experience pain or discomfort.
- You have a wart that persists despite treatment.
- The wart is located in sensitive areas, such as the face or genitals.
Conclusion
Wart removal can be a straightforward process, but the best approach depends on the type of wart, its location, and individual preferences. With various treatment options available, individuals can choose what best suits their needs. Additionally, adopting preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing warts in the first place. If you have concerns about warts or need assistance with removal, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Yes, warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which can spread through direct contact with a wart or surfaces contaminated with the virus.
Yes, many warts will eventually go away without treatment, although this process may take months or even years.
Some methods of wart removal, such as cryotherapy or electrosurgery, can be painful, while others, like topical treatments, may cause minimal discomfort.
Over-the-counter treatments are available for home use, but it’s essential to follow the instructions carefully. If in doubt, consult a healthcare professional.
The duration of treatment can vary depending on the method used. Some warts may require multiple sessions for complete removal.
Possible side effects include pain, redness, blistering, or scarring. Discuss potential risks with your healthcare provider before proceeding with treatment.
Yes, warts can recur even after successful removal, especially if the virus remains in the body.
Home remedies such as duct tape, apple cider vinegar, and garlic may help some individuals, but their effectiveness varies.
While warts are typically harmless, treatment may be necessary for cosmetic reasons or if they cause pain or discomfort.
It’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for appropriate treatment options, as some methods may not be suitable for facial warts.
