Introduction
Warts are benign skin growths caused by an infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can appear in various shapes and sizes, often resembling small bumps or rough patches on the skin. While warts are usually harmless, many people choose to have them removed for cosmetic reasons or because they cause discomfort. This article will explore the causes of warts, various treatment options, home remedies, and preventive measures to help you manage and remove skin warts effectively.
Understanding Warts
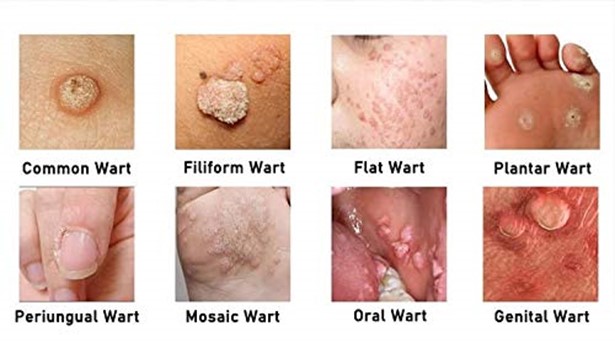
Warts can appear on different parts of the body and are classified into several types, each with unique characteristics:
Common Warts
- Appearance: Common warts are raised, rough bumps that typically appear on the fingers, knees, and elbows.
- Color: They may be gray or brown and often have a rough surface.
- Causes: Caused by HPV, they can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact or by touching contaminated surfaces.
Plantar Warts
- Appearance: Plantar warts occur on the soles of the feet and can be flat due to pressure.
- Characteristics: They may have a hard center surrounded by a thickened layer of skin.
- Discomfort: Plantar warts can be painful, especially when walking, due to their location.
Flat Warts
- Appearance: These warts are smaller and smoother than common warts and often occur in clusters.
- Common Locations: They typically appear on the face, neck, and forehead.
- Children and Teens: Flat warts are more common in children and adolescents.
Genital Warts
- Transmission: Genital warts are sexually transmitted and can appear in the genital area.
- Health Risks: Certain strains of HPV that cause genital warts can lead to cervical and other types of cancers.
Causes of Warts
Warts are primarily caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). This virus has over 100 different strains, with some causing common skin warts, while others lead to genital warts. Warts can spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces, such as swimming pool decks or gym locker rooms. Additionally, factors that may increase the risk of developing warts include:
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to HPV infections.
- Personal Habits: Activities such as nail-biting or shaving can create small cuts or abrasions, allowing the virus to enter the skin.
- Skin-to-Skin Contact: Warts can spread easily through skin-to-skin contact with an infected person.
Diagnosis of Warts
Diagnosing warts is generally straightforward. Healthcare providers can usually identify warts through visual examination. In some cases, they may perform a biopsy to rule out other skin conditions or confirm the diagnosis. If a wart changes in appearance or does not respond to treatment, further evaluation may be necessary.
Treatment Options for Warts
While many warts resolve on their own without treatment, various options are available for those seeking removal. Treatment methods can be categorized into medical procedures and home remedies.
Medical Treatments
1.Cryotherapy
- Procedure: Cryotherapy involves freezing the wart using liquid nitrogen.
- Effectiveness: This treatment causes the wart tissue to die and eventually fall off, typically requiring multiple sessions.
- Discomfort: Patients may experience a burning sensation during the procedure and slight swelling afterward. Pain relief measures can be used as necessary.
2.Salicylic Acid
- Over-the-Counter Treatment: Salicylic acid is a common topical treatment for warts, available over-the-counter.
- Mechanism: It works by gradually peeling away the wart layer by layer.
- Application: Patients should apply the product daily, ideally after soaking the wart in warm water. It may take several weeks to months for the wart to disappear completely.
3.Electrosurgery
- Technique: Electrosurgery uses high-frequency electrical currents to burn off the wart.
- Anesthesia: This procedure typically requires local anesthesia and is effective for larger warts.
- Aftercare: Post-procedure care is essential to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of infection.
4.Laser Treatment
- Focused Light Therapy: Laser therapy targets the wart with focused light, effectively destroying the wart tissue.
- Suitability: This method is often used for stubborn warts that do not respond to other treatments.
- Sessions Required: Patients may require multiple sessions, and pain management is often provided during and after treatment.
5.Immunotherapy
- Stimulation of Immune Response: Immunotherapy involves using medications to stimulate the immune system to fight off the HPV virus.
- Administration: A healthcare provider may use topical treatments or injections to enhance the immune response.
- Effectiveness: This method can be effective for warts that are resistant to traditional treatments.
6.Surgical Excision
- Indication: For larger warts or those that do not respond to other treatments, surgical excision may be necessary.
- Local Anesthesia: The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and the wart is cut out using a scalpel.
- Post-Surgery Care: Proper care and hygiene are crucial to prevent infection and promote healing.
Home Remedies for Wart Removal
Many individuals opt for home remedies to treat warts, although their effectiveness varies. Here are some commonly used home treatments:
1. Apple Cider Vinegar
- Antiviral Properties: Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is believed to have antiviral properties.
- Application: Soak a cotton ball in ACV and place it on the wart, covering it with a bandage. This should be done daily until the wart falls off.
- Skin Irritation: Users should monitor for skin irritation, as ACV can cause redness or burning sensations.
2. Garlic
- Natural Antiviral: Garlic contains allicin, which is thought to have antiviral properties.
- Method: Applying crushed garlic directly to the wart and covering it with a bandage may aid in removal.
- Caution: Similar to ACV, garlic may cause skin irritation, so users should watch for any adverse reactions.
3. Banana Peel
- Enzymatic Action: The inside of a banana peel is rich in enzymes that may help break down wart tissue.
- Usage: Rubbing the inside of the peel on the wart or placing it on the wart overnight can promote its removal.
4. Tea Tree Oil
- Antimicrobial Properties: Tea tree oil is known for its antimicrobial properties.
- Application: Dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil and apply it directly to the wart. Cover with a bandage for best results.
- Monitoring: Watch for any irritation or allergic reactions.
5. Duct Tape
- Occlusion Therapy: Some individuals find success using duct tape as a wart removal method.
- Method: Covering the wart with duct tape for several days may suffocate it and promote its fall-off.
- Duration: Change the tape regularly and keep the area dry for optimal results.
6. Vitamin E
- Skin Healing: Vitamin E is thought to promote skin healing.
- Method: Applying vitamin E oil directly to the wart may support its removal over time.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While many wart removal treatments are generally safe, there are potential risks and side effects to consider:
- Skin Irritation: Topical treatments like salicylic acid, ACV, and natural remedies can cause skin irritation, redness, or blistering.
- Infection: Any procedure that breaks the skin can potentially lead to infection. Keeping the area clean and following post-treatment care is essential.
- Scarring: Some wart removal methods, particularly surgical excision, may result in scarring, especially if not properly cared for during the healing process.
Prevention of Warts
Preventing warts involves minimizing exposure to the HPV virus and adopting healthy skin habits:
- Avoid Skin-to-Skin Contact: Refrain from touching warts on yourself or others. Use protective barriers, like gloves, when treating warts.
- Keep Your Skin Healthy: Maintain good hygiene and keep your skin moisturized to prevent breaks that may allow the virus to enter.
- Use Footwear in Public Areas: Wearing shoes in communal areas, like swimming pools and locker rooms, can reduce the risk of plantar warts.
- Avoid Nail Biting: This habit can create breaks in the skin, increasing the risk of HPV infection.

When to See a Doctor
It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider if:
- The wart changes in appearance or size.
- It becomes painful or bleeds.
- You experience multiple warts.
- The wart persists despite home treatment.
- You are unsure whether a skin growth is a wart or another condition.
Conclusion
Removing skin warts is a common concern for many individuals. While warts are generally harmless, they can be bothersome and unsightly. Understanding the available treatment options, including medical procedures and home remedies, is crucial for effective wart removal. If you're struggling with warts, consider consulting a healthcare provider for tailored advice and treatment options that suit your needs. Remember that prevention is the best strategy, so adopt healthy habits to minimize your risk of developing warts in the future.
Yes, warts can spread through skin-to-skin contact or by touching surfaces contaminated with the HPV virus. They are more likely to spread in moist environments, such as swimming pools.
While some home remedies may work, it is recommended to consult a healthcare provider for safe and effective treatment options, especially for larger or more persistent warts.
Warts can resolve on their own within months to years. However, treatment can expedite the process, and some warts may require several sessions to disappear completely.
Warts are generally painless, but plantar warts can be uncomfortable or painful, especially when pressure is applied during walking or standing.
Preventive measures include maintaining good hygiene, avoiding skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals, and protecting your feet in communal areas.
Warts can recur, especially if the HPV virus remains in the body. Proper treatment can minimize the likelihood of recurrence, but it is essential to monitor for new growths.
No, picking at warts can spread the virus to other areas of your skin and may lead to infection. It is best to leave the wart alone or seek professional treatment.
Potential side effects include skin irritation, redness, blistering, and, in some cases, scarring. Following post-treatment care instructions can help reduce these risks.
No, warts are benign and do not turn into cancer. However, it is essential to differentiate between warts and other skin lesions that may require further evaluation by a healthcare provider.
The best method depends on the wart's type, size, and location. Consulting a healthcare provider can help determine the most suitable treatment option tailored to your needs.
