Introduction
Hair loss is a common concern that affects millions of individuals around the world. For those looking to restore their hair, Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT) presents a viable surgical solution. This detailed article explores the intricacies of FUT, its procedure, benefits, risks, post-operative care, and what individuals can expect during their hair restoration journey.
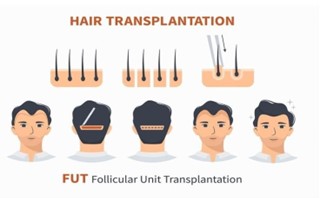
Understanding Hair Loss
Types of Hair Loss
Hair loss can manifest in various forms, primarily categorized as:
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Often referred to as male or female pattern baldness, this hereditary condition affects millions, leading to gradual thinning and eventual loss of hair.
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder that causes sudden hair loss in patches. The hair may regrow in some cases, but the condition can be unpredictable.
- Telogen Effluvium: A temporary form of hair loss resulting from stress, hormonal changes, or nutritional deficiencies, leading to increased shedding.
- Traction Alopecia: Caused by hairstyles that pull on the hair shaft, leading to gradual hair loss.
- Scarring Alopecias: Conditions that lead to permanent hair loss due to inflammation that damages the hair follicles.
Understanding the underlying cause of hair loss is essential for determining the appropriate treatment. This is where surgical methods like FUT can be beneficial.
What is Follicular Unit Transplant?
Follicular Unit Transplant is a surgical procedure designed to restore hair by relocating hair follicles from a donor site, typically at the back of the head, to balding or thinning areas. FUT focuses on the natural grouping of hair follicles, allowing for a seamless and natural appearance post-transplant.
The Science Behind Follicular Units
Follicular units are the natural anatomical structures of hair, consisting of one to four hair follicles, along with sebaceous glands and connective tissue. By transplanting these units in their natural groupings, FUT aims to replicate the way hair grows naturally on the scalp, resulting in fuller and more aesthetically pleasing hair.
The FUT Procedure: Step-by-Step
The FUT procedure is meticulously planned and executed. Below is a detailed breakdown of each step involved in the process:
1. Initial Consultation
The first step in the FUT process is a thorough consultation with a qualified hair restoration surgeon. During this appointment, the surgeon assesses:
- Hair Loss Pattern: Understanding the extent of hair loss and its pattern is crucial for designing a personalized treatment plan.
- Medical History: A comprehensive medical history helps identify any underlying health issues that might affect surgery and healing.
- Expectations: Discussing realistic outcomes and setting expectations is vital for patient satisfaction.
2. Preparation on the Day of Surgery
On the day of the procedure, patients are advised to avoid certain medications that may increase bleeding. The surgical team prepares the patient by:
- Cleaning the Scalp: The scalp is thoroughly cleansed to minimize the risk of infection.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the donor and recipient areas, ensuring the patient’s comfort throughout the surgery.
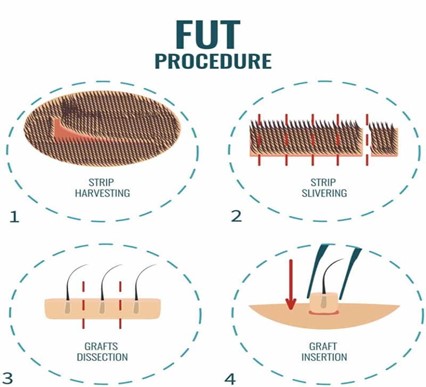
3. Harvesting the Donor Strip
In FUT, a strip of scalp, typically ranging from 6 to 10 inches long, is carefully excised from the donor area. This strip contains hair follicles that will be relocated to balding areas. The extraction process includes:
- Dissection: After harvesting, the strip is carefully dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope. This meticulous approach is critical for ensuring the survival of each graft.
- Closure of Donor Site: The donor site is then closed using sutures, leaving a linear scar that is usually concealed by surrounding hair.
4. Creating Recipient Sites
Once the grafts are prepared, the surgeon creates small incisions in the recipient area where the hair will be implanted. Key considerations include:
- Natural Hairline Design: The surgeon aims to replicate the natural hairline, taking into account the patient’s facial features and hair growth patterns.
- Graft Angle and Direction: Proper angling and direction of grafts are crucial for achieving a natural look.
5. Implantation of Follicular Units
The prepared grafts are then meticulously implanted into the recipient sites. This phase involves:
- Placing Grafts: Each follicular unit is inserted one by one into the recipient areas, with careful attention to density and spacing.
- Duration: Depending on the number of grafts, this process can take several hours, typically ranging from 4 to 8 hours.
6. Post-Operative Care and Instructions
After the procedure, patients receive specific post-operative care instructions to facilitate healing and ensure optimal results:
- Caring for the Transplanted Area: Instructions on how to wash the hair, avoid touching the grafts, and care for the scalp are provided.
- Medications: Patients may be prescribed antibiotics and pain relievers to manage discomfort and prevent infection.
Benefits of Follicular Unit Transplant
FUT offers a range of advantages that make it an appealing choice for hair restoration:
1. Natural-Looking Results
One of the standout benefits of FUT is the natural appearance of the results. By transplanting hair in its natural follicular units, patients can achieve a seamless blend with existing hair.
2. High Graft Yield
FUT allows for a higher number of grafts to be harvested in a single session compared to other techniques, making it ideal for individuals with significant hair loss.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Generally, FUT is less expensive than FUE because it is a more efficient procedure that can yield a higher number of grafts in a shorter time frame.
4. Effective for Advanced Hair Loss
FUT is particularly beneficial for individuals experiencing advanced stages of hair loss, providing substantial coverage in one surgical session.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While FUT is considered safe, it is essential to acknowledge potential risks and side effects:
1. Scarring
FUT leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which may be visible if hair is cut short. However, most patients find that the scar is well-concealed by surrounding hair.
2. Infection
Although rare, infections can occur post-surgery. Adhering to post-operative care instructions minimizes this risk.
3. Bleeding and Swelling
Some patients may experience minor bleeding and swelling in the donor and recipient areas, which usually resolves within a few days.
4. Unsatisfactory Results
In some cases, patients may not achieve the desired density or coverage, necessitating additional procedures.
5. Temporary Shock Loss
Some patients may experience temporary hair loss around the transplanted area. This is generally temporary and resolves as the scalp heals.
Post-Operative Care: Ensuring Success
Proper post-operative care is crucial for achieving the best results from FUT. Here are some essential care tips:
1. Follow Instructions
Adhere to the surgeon’s post-operative care instructions, which may include how to wash your hair, avoid certain activities, and apply any prescribed topical treatments.
2. Avoid Physical Activity
Patients are advised to refrain from strenuous physical activities for at least a week following the procedure to prevent strain on the scalp and allow for proper healing.
3. Medication
Take any prescribed medications as directed to manage discomfort and prevent infection. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also be recommended.
4. Monitor for Complications
Watch for signs of infection, unusual swelling, or excessive bleeding. Contact the surgeon immediately if any concerns arise.
Results and Expectations
Patients can expect to see initial hair growth within a few months post-surgery. However, full results may take up to a year to manifest. It’s essential to maintain realistic expectations regarding the outcome, as individual results can vary based on factors like hair type, age, and the extent of hair loss.
Alternatives to FUT
While FUT is an effective option for many, there are alternatives available, including:
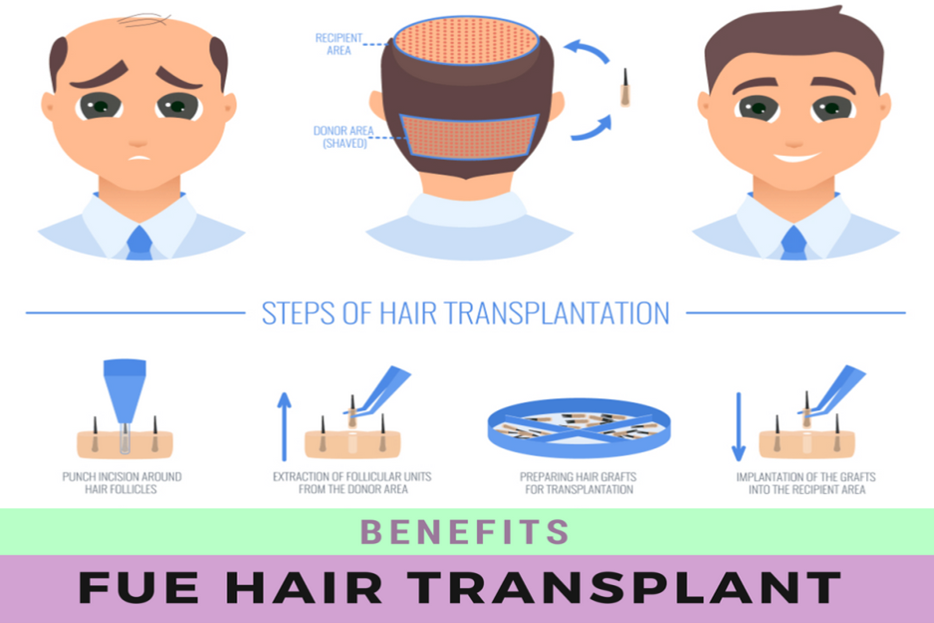
1. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a minimally invasive technique that involves extracting individual hair follicles from the donor area without the need for a strip. This method leaves minimal scarring and offers quicker recovery times. However, it is generally more time-consuming and expensive than FUT.
2. Non-Surgical Treatments
Medications such as minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) can help slow hair loss and promote regrowth. While effective for some individuals, these medications are often less effective than surgical options for advanced hair loss.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting a concentration of platelets derived from the patient’s blood into the scalp to promote hair growth. While non-surgical, it may not provide the same level of results as FUT and typically requires multiple sessions.
Considerations Before Undergoing FUT
1. Candidacy
Not everyone is a suitable candidate for FUT. Ideal candidates have stable hair loss patterns and realistic expectations. Consulting a specialist can help determine the best approach.
2. Age
Younger patients may face progressive hair loss, which could affect the long-term results of transplants. It’s crucial to consider future hair loss when planning for FUT.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Post-surgery lifestyle changes, such as avoiding vigorous physical activity and exposure to direct sunlight, may be necessary for optimal recovery.
4. Psychological Readiness
Undergoing hair restoration is a significant decision that can impact self-esteem. It’s essential to ensure that you are mentally prepared for the journey and potential outcomes.
Conclusion
Follicular Unit Transplant stands out as a reliable and effective solution for those grappling with hair loss. By understanding the procedure, its benefits, and potential risks, individuals can make informed decisions about their hair restoration options. As techniques and technology continue to advance, FUT remains a leading choice for achieving natural and lasting results in hair restoration.
FUT is most suitable for individuals with stable hair loss patterns and sufficient donor hair. A consultation with a specialist is essential.
The procedure typically lasts between 4 to 8 hours, depending on the number of grafts being transplanted.
Most patients can return to their normal activities within a week, although complete healing may take several weeks.
It is common for transplanted hair to shed within the first few weeks after surgery. New growth typically begins within 3-4 months.
Yes, FUT can be combined with other treatments like PRP therapy for enhanced results.
If you don't have enough donor hair, your doctor may recommend alternative hair loss treatments, such as medication or hair restoration devices.
Some patients may require multiple sessions to achieve the desired density, especially if they have extensive hair loss.
Yes, women can also benefit from FUT, especially those experiencing pattern baldness.
Avoid vigorous exercise, heavy lifting, and direct sun exposure for at least a week post-surgery.
Follow all post-operative care instructions, maintain realistic expectations, and consult your surgeon if you have any concerns during recovery.
