Introduction
Warts are benign, usually painless growths on the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They can occur on any part of the body, including the hands, feet, face, and genital areas. While warts are generally harmless, they can be unsightly or uncomfortable, prompting many individuals to seek removal. This article delves into various wart removal procedures, how they work, their effectiveness, potential side effects, and essential aftercare.
Understanding Warts
What Are Warts?
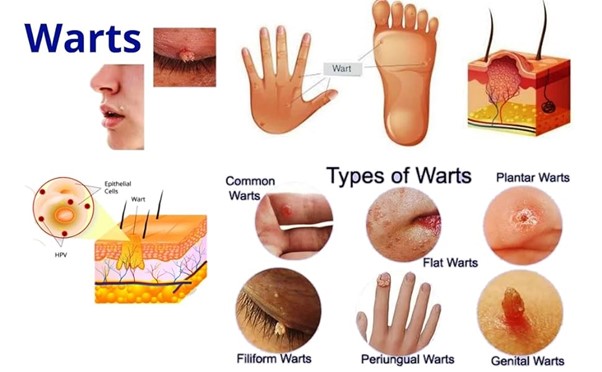
Warts are small, raised bumps on the skin that vary in size, shape, and color. They can be rough or smooth and are often mistaken for other skin conditions. Warts can be classified into several types:
- Common Warts: Typically found on the hands, fingers, and elbows, common warts have a rough surface and can appear anywhere on the body.
- Plantar Warts: These occur on the soles of the feet and can be painful due to the pressure from walking. They may have a callused surface.
- Flat Warts: Smaller and smoother than other types, flat warts can occur in groups and are often found on the face, arms, and legs.
- Filiform Warts: These are thread-like warts that usually appear around the mouth, nose, or on the neck.
- Genital Warts: These are sexually transmitted and occur in the genital and anal areas.
Causes of Warts
Warts are primarily caused by HPV, which infects the outer layer of skin. The virus enters through cuts or breaks in the skin. Once inside, it causes rapid skin cell growth, leading to the formation of warts. Factors that can increase the likelihood of developing warts include:
- Direct Contact: Touching a wart or skin infected with HPV can spread the virus to others.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to warts.
- Moist Environments: HPV thrives in warm, moist environments, making places like swimming pools and communal showers hotspots for infection.
Wart Removal Procedures
Various methods are available for wart removal, and the effectiveness of each procedure may vary based on the wart type, location, and individual preferences. Here’s an in-depth look at the most common wart removal procedures:
1. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is one of the most widely used wart removal methods. It involves freezing the wart using liquid nitrogen. This process is often performed in a healthcare provider's office and usually takes just a few minutes.
How It Works: The healthcare provider applies liquid nitrogen to the wart, causing it to freeze. This freezing action leads to the formation of a blister beneath the wart, which eventually causes the wart to fall off.
Pros:
- Effectiveness: Cryotherapy is highly effective for many types of warts, particularly common and plantar warts.
- Quick Procedure: The treatment is relatively quick, usually taking only a few minutes.
- Minimal Pain: Most patients experience little to no pain during the procedure, although some report a mild burning sensation.
Cons:
- Multiple Sessions: Some patients may require several treatments to achieve complete removal.
- Post-Treatment Effects: Patients may experience blistering, redness, or swelling in the treated area.
2. Electrosurgery and Curettage
Electrosurgery and curettage is a procedure that combines two techniques: electrosurgery, which uses high-frequency electrical currents to burn the wart, and curettage, which involves scraping the wart off with a small surgical instrument.
How It Works: In this procedure, the healthcare provider first numbs the area with local anesthesia. They then use electrosurgery to burn the wart, followed by curettage to scrape it off.
Pros:
- Effectiveness: This method is often successful for larger or more stubborn warts.
- Quick Results: The procedure usually takes only a few minutes, and patients often see immediate results.
Cons:
- Scarring: There is a risk of scarring or changes in skin pigmentation after the procedure.
- Anesthesia Required: The use of local anesthesia can cause discomfort for some patients.
3. Laser Treatment
Laser therapy is a more advanced method for removing warts. It uses concentrated light to target and destroy the wart tissue.
How It Works: The healthcare provider directs a laser beam at the wart, which heats and destroys the wart tissue without damaging surrounding skin.
Pros:
- Precision: Laser treatment allows for precise targeting of the wart while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Effective for Resistant Warts: This method is particularly useful for warts that have not responded to other treatments.
Cons:
- Cost: Laser treatment is typically more expensive than other methods.
- Multiple Sessions: Some patients may require several sessions for complete removal.
4. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve applying a solution containing salicylic acid or other chemical agents to the wart. This process helps to exfoliate the wart tissue gradually.
How It Works: Patients may use over-the-counter products containing salicylic acid at home, or a healthcare provider may apply a stronger solution in their office. The chemical gradually breaks down the wart tissue, allowing it to be removed.
Pros:
- Accessibility: This method is easy to use and can be done at home.
- Gradual Removal: The gradual process minimizes discomfort compared to more invasive treatments.
Cons:
- Longer Results: It may take longer to see results compared to other methods.
- Consistency Required: Patients must consistently apply the treatment for effectiveness.
5. Surgical Excision
In some cases, surgical excision may be necessary, especially for large or persistent warts. During this procedure, the wart is cut out using a scalpel.
How It Works: The healthcare provider numbs the area, then uses a scalpel to cut out the wart along with a small margin of surrounding skin.
Pros:
- Immediate Results: Surgical excision provides immediate results, suitable for larger warts.
- Comprehensive Removal: This method can effectively remove the entire wart, reducing the chance of recurrence.
Cons:
- Invasive Procedure: Surgical excision is more invasive and has a longer recovery time compared to other methods.
- Scarring Risk: There is a higher risk of scarring and infection with surgical excision.
6. Home Remedies
While many people opt for professional treatments, some prefer to try home remedies. Common home treatments include:
Apple Cider Vinegar: Soaking a cotton ball in apple cider vinegar and applying it to the wart may help dissolve the wart over time.
Duct Tape: Covering the wart with duct tape for several days may promote removal.
Tea Tree Oil: This essential oil has antiviral properties and may help to eliminate warts when applied regularly.
Pros:
- Convenient and Cost-Effective: Home remedies are generally inexpensive and easy to access.
- Non-Invasive: These methods are non-invasive and can be done in the comfort of your home.
Cons:
- Effectiveness Varies: The success of home remedies varies from person to person.
- Time-Consuming: Results may take longer to achieve compared to professional treatments.
Post-Removal Care
Proper aftercare is crucial after any wart removal procedure to promote healing and prevent infection. Here are some general aftercare tips:
- Keep the Area Clean: Gently wash the treated area with mild soap and water. Avoid scrubbing, as this can irritate the skin.
- Apply a Bandage: If recommended by your healthcare provider, cover the area with a bandage to protect it from dirt and bacteria.
- Avoid Picking or Scratching: It’s essential to resist the urge to touch the area to prevent irritation or infection.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection: Watch for increased redness, swelling, or discharge, which could indicate infection. If any of these occur, contact your healthcare provider.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend any scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor healing and address any concerns.
Conclusion
Wart removal procedures are effective in eliminating bothersome growths and improving the skin's appearance. With various treatment options available, individuals can choose the method that best suits their needs and preferences. It's essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach for your specific situation. Whether opting for cryotherapy, electrosurgery, or home remedies, understanding the options and following proper aftercare will contribute to a successful wart removal experience.
By taking proactive steps to treat and prevent warts, individuals can maintain their skin's health and appearance, freeing themselves from the worry and discomfort these growths can cause.
Yes, warts are contagious and can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or surfaces contaminated with the virus.
Many warts will resolve without treatment, but this can take months or even years.
While some home remedies exist, professional treatments are generally safer and more effective.
Most procedures involve minimal discomfort, especially with local anesthesia or numbing agents.
Most wart removal procedures can be completed in a few minutes, although recovery time may vary.
Warts can recur, particularly if a person is prone to developing them. However, treated warts do not grow back.
It’s advisable to avoid elective procedures during pregnancy. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Mild redness and swelling are common after removal. Most individuals can return to normal activities shortly after the procedure.
Possible side effects include scarring, infection, and changes in skin pigmentation, although these are rare.
Maintaining good hygiene, avoiding direct contact with warts, and wearing flip-flops in public showers can help reduce the risk of developing warts.
