Understanding the Difference Between FUT and FUE Hair Transplants
Hair loss is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide, impacting both men and women of all ages. Whether caused by genetics, hormonal changes, stress, or medical conditions, hair thinning and balding can significantly affect self-confidence and overall appearance. Fortunately, modern hair restoration techniques have evolved to offer effective, long-lasting solutions—among which FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) and FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) are the most popular.
If you’re considering a hair transplant, understanding the differences between FUT and FUE is essential to making an informed decision. Each method has its own advantages, drawbacks, and suitability depending on your goals, hair type, and medical history. This blog will help you understand both procedures, how they work, what recovery looks like, and which option may be better for your needs.
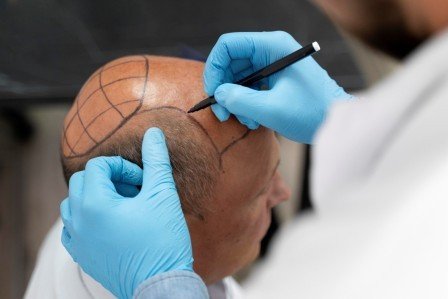
What Is FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation)?
FUT, sometimes referred to as the strip method, is a traditional technique that involves removing a small strip of scalp—usually from the back of the head—where hair growth is typically denser and unaffected by balding. The strip is then dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope and transplanted into areas of hair loss.
How FUT Works:
- Strip Removal: A narrow strip of skin is surgically removed from the donor area.
- Suturing: The area is closed with stitches, which usually leaves a linear scar.
- Dissection: The strip is divided into individual follicular units (grafts).
- Transplantation: Grafts are carefully placed into the recipient area (thinning or balding zones).
Key Benefits of FUT:
- Typically allows more grafts in a single session, ideal for extensive hair loss.
- Often lower cost compared to FUE.
- Preserves the donor area's density better for those needing multiple procedures.
- Proven track record and widely used for over two decades.
Limitations of FUT:
- Leaves a linear scar at the back of the head.
- Longer recovery time compared to FUE.
- May limit short hairstyles due to scar visibility.
- Potential for post-surgical discomfort and tightness.
What Is FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)?
FUE is a newer, more advanced hair transplant method that involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a specialized micro-punch tool. Each follicular unit is then implanted into the recipient area without the need for stitches or a strip of skin removal.
How FUE Works:
- Shaving: The donor area is trimmed or shaved for visibility.
- Extraction: Individual follicular units are removed using a punch tool (typically 0.7–1.0 mm in diameter).
- Graft Preparation: The follicles are cleaned and prepared for implantation.
- Transplantation: Grafts are placed into the balding or thinning areas.
Key Benefits of FUE:
- No linear scar—makes it ideal for short haircuts or buzz cuts.
- Minimally invasive with a faster recovery.
- Less discomfort and fewer post-op complications.
- Great for patients wanting a more discreet treatment.
Limitations of FUE:
- Takes longer than FUT (especially for large areas).
- May be more expensive due to its labor-intensive nature.
- Risk of overharvesting if not performed properly.
- May yield fewer grafts per session.
Comparing FUT and FUE: Which Hair Transplant Method Is Right for You?
1. Technique
- FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): Involves surgically removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, from which hair grafts are extracted and implanted into thinning or balding areas.
- FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Involves the direct extraction of individual hair follicles from the donor site using a micro-punch tool—no strip removal or stitches required.
2. Scarring
- FUT: Leaves a thin linear scar at the donor site. The scar is typically concealed by longer hair but may be visible with very short hairstyles.
- FUE: Results in multiple tiny dot scars that are barely noticeable, even with shorter haircuts.
3. Recovery Time
- FUT: Recovery may take 10–14 days. Patients might experience tightness or discomfort around the donor area due to stitches.
- FUE: Recovery is quicker, typically around 5–7 days, with less discomfort and no need for stitches.
4. Hair Graft Yield
- FUT: Allows for the harvesting of a higher number of grafts in a single session—making it well-suited for individuals with more significant hair loss.
- FUE: Suitable for moderate hair thinning or small, targeted areas. While fewer grafts are extracted per session, the results are natural and effective.
5. Pain and Discomfort
- FUT: May result in more discomfort during the healing process, especially at the back of the scalp where the strip was removed.
- FUE: Generally causes less post-operative pain. The micro-wounds are small, and most patients return to daily activities sooner.
6. Ideal Candidate
- FUT: Ideal for individuals who need maximum grafts and are comfortable with a linear scar that can be hidden by longer hair.
- FUE: Best for those seeking minimal scarring, quicker recovery, and flexibility with short hairstyles.
Which Is Better: FUT or FUE?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer—it depends entirely on the patient’s goals, budget, lifestyle, and medical factors.
Choose FUT If:
- You need a large number of grafts in one session.
- You plan to keep your hair long (scar will be hidden).
- You're looking for cost-effective treatment.
- You don’t mind a linear scar.
Choose FUE If:
- You prefer short hairstyles or want no visible scarring.
- You seek a faster recovery.
- You need minor or moderate coverage.
- You want a more discreet, minimally invasive experience.
Pain, Recovery, and Healing Process
FUT Recovery:
- Requires stitches, which are removed after 10–14 days.
- Swelling and soreness are more common.
- Healing of the donor area takes longer.
- Patients advised to avoid strenuous activity for 2–3 weeks.
FUE Recovery:
- No stitches, minimal pain.
- Scalp may feel tight or itchy for a few days.
- Tiny scabs fall off in about 7–10 days.
- Most people return to normal activity within 5–7 days.
Pain is manageable in both methods and usually subsides within a week.
Scarring and Hair Style Considerations
One of the most important aesthetic concerns is scarring:
- FUT leaves a thin linear scar, which can be concealed with longer hair.
- FUE results in many micro-dots that are barely visible, making it perfect for fades, undercuts, and short hairstyles.
If you frequently wear short hair or wish to avoid any visible marks, FUE is the better option.
Long-Term Results
Both FUT and FUE offer permanent and natural-looking results when performed by an experienced surgeon. The transplanted hairs are genetically resistant to balding, meaning they’ll typically remain in place for a lifetime.
However, long-term results depend on:
- Surgeon skill and precision
- Post-operative care
- Overall health and scalp condition
- Avoiding future trauma or illness affecting hair
Results from both techniques usually become noticeable within 6 to 9 months, with full results in 12–15 months.
While FUT may seem more affordable upfront, some patients consider the aesthetic advantage of FUE worth the investment.
Are There Risks With Either Procedure?
Both procedures are generally safe, especially when performed by qualified surgeons. However, like all surgeries, risks include:
- Infection
- Swelling or bleeding
- Poor hair growth if not done correctly
- Follicle shock loss (temporary shedding)
- Uneven hairline or unnatural results with unskilled practice
Selecting a reputable clinic with proven expertise is critical to avoiding complications.
Choosing the Right Hair Transplant Technique
When deciding between FUT and FUE, consider:
- Your age and degree of hair loss
- The availability of donor hair
- Your desired hairstyle
- Your comfort with scarring
- Your budget and time constraints
A thorough consultation with a hair restoration specialist can help assess your scalp and design a personalized treatment plan. In some cases, a combined approach using both FUT and FUE may be recommended for optimal density and coverage.
Final Thoughts
FUT and FUE are both effective, proven methods of restoring natural hair growth in balding or thinning areas. Understanding the core differences—particularly in terms of scarring, recovery, cost, and suitability—is essential for making the right decision.
- FUT offers high graft yields and is cost-effective but leaves a visible scar.
- FUE provides minimal scarring and faster healing but may take longer and cost more.
Choosing the right technique depends on your unique goals and needs. Whichever path you choose, a successful hair transplant can restore your confidence, rejuvenate your appearance, and give you a permanent solution to hair loss.